Aja Frost on AI search, content strategy, and AEO success metrics

Google’s AI Overviews and AI-driven search are reshaping content creation, SEO, and user behavior.
As we watch this fascinating evolution of search – and continue to debate what we call this new marketing discipline (HubSpot is opting for AEO, or answer engine optimization) – I interviewed Aja Frost, senior director of global growth and paid media at HubSpot. Some of the topics covered in our interview:
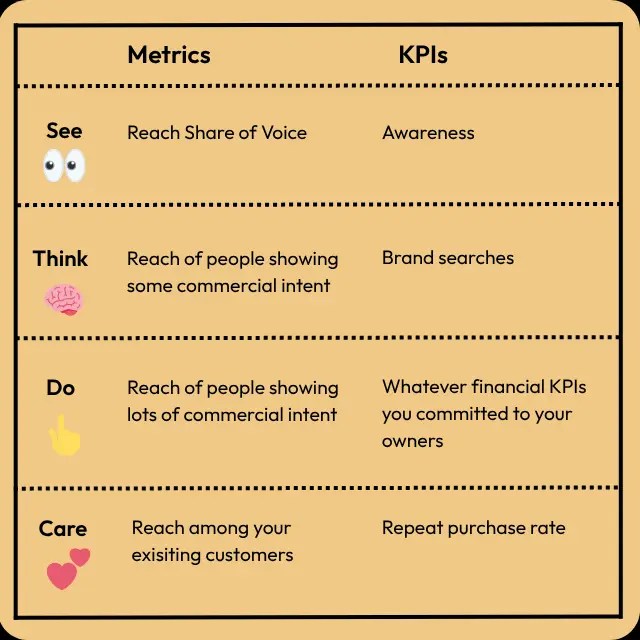
- The need to redefine success metrics for AEO, prioritizing visibility and share of voice
- HubSpot’s experimental journey, including creating hyperspecific, data-rich content and optimizing for LLMs.
- Traffic directly from LLMs converts about 3x better than traditional search traffic for HubSpot.
This transcript has been edited for length and clarity.
Danny Goodwin:
Hey everybody, this is Danny Goodwin, editorial director of Search Engine Land, and, today I’m being joined by Aja Frost. We have an interesting discussion coming up about GEO, AEO, AI, and all the good hot topics. It’s great to meet you Aja. ’cause I’ve actually never, uh, run into you on the conferences or anywhere. So it’s really nice to connect with you.
Aja Frost:
You know, Danny, I was gonna say, it’s nice to see you, which is my go-to if I’m not sure whether I’ve seen someone, I met someone before. I figured we had met because we definitely run in the same circles. But I’m delighted to be finally, officially making your acquaintance.
Danny Goodwin:
Absolutely. Before we dive in for the people watching or listening, do you want to introduce yourself? Tell us a little bit about who you are and what you do?
Aja Frost:
Yep. I am Senior Director of Global Growth and Paid Media at HubSpot. Global Growth is our catch-all for top-of-funnel non-paid demand, which largely translates to SEO and now AEO. And I’ve been at HubSpot for a little over nine years, which is about eight years longer than I thought I would be. For those who don’t know, HubSpot is the customer platform that powers 268,000 teams. And it changes, I would say, as a company, every few years, which is what has kept me there. I think we have had a really interesting journey to this point, and we are embarking on what I believe is the most interesting era of SEO, AEO, and really marketing yet.
Danny Goodwin:
Absolutely. So, yeah, it is a very fun time and you’ve been around for a few years at this point, so very curious to get your take. So, we had SMX Advanced a while back, our conference returned in person and at that point in time I’m like, oh, this whole a AEO versus GEO versus whatever we’re gonna call a debate – it’s gotta be settled by the time like October, November comes around. And I’m surprised that it has not still been settled. So I’m curious from your perspective, where do you stand on that whole name debate? What are you calling it, you know, this new form of SEO, or if it’s some, even if you consider it a new form of SEO, you know, has been GEO, AEO, some people call it AI SEO. What are you kind of calling this practice right now internally and, and why have you settled on whatever term that is?
Aja Frost:
Yeah, great question because this was the topic of much debate internally at HubSpot. I think we debated all of the names that you just mentioned and probably 10 more. And we ultimately landed on AEO, or answer engine optimization, because we think it best reflects how people are using AI and what businesses/brands should be doing in response. So I think SEO, you wanted to rank in the results, like that was pretty clear. Now you wanna be a part of the answer. And so answer engine optimization is the tactics, the plays that you run to show up as part of that answer. Also, it just sounds cooler than GEO in my opinion, but we’ll see how long the debate rages on. I have learned not to underestimate how long people in our particular world can spend haggling and debating this type of thing.
Danny Goodwin:
Yes, I know it’s, it’s sort of like subdomains versus subfolders. If you’ve been around long enough, you’ll know what that means and how long that debate has been going on. And I can’t even tell you, uh, more than a decade, I’m safe in assuming. Whatever we call it ultimately or whatever it gets decided it is called, this does feel like a big transition point for search from traditional ranking search to AI search is more about retrieval. So for you, how has it changed the way you’re thinking about visibility and strategy?
Aja Frost:
Yeah, we are very much thinking about AEO as an evolution of SEO, which I did my homework and I’m just a Danny Goodwin fan, so I know that I think we’re on the same page there. And yes, that was an intentional pun. I think one thing that has actually always been a very HubSpot philosophy is do what’s best for the customer. And that’s always overlapped really neatly with our SEO strategy. It’s also what Google has preached for many years – do what’s best for the customer. You may miss out on some short-term wins, but in the long run, your site is going to perform better. And that is at the heart of our AEO strategy. I also think that the three buckets of plays that we’re running are familiar from SEO.
So the what hasn’t changed, but the how has, and I’ll go a click deeper there. Those three buckets for us are content, technical, and offsite.
Our content for AEO looks fairly different than it does for SEO. It’s much more specific. It’s much nicher and deeper. It’s structured differently. It’s written differently. But it’s always intended to be what’s best for the customer or best for the reader.
The second bucket is technical. And again, I think that Google indexes/ingests content differently than AI bots do. And so we need to adjust our technical strategies to match while not doing anything that’s harmful for GoogleBot, because of course we still care about Google.
And then offsite, one thing that is probably the clearest from SEO to AEO is the emphasis on brand mentions rather than links. And so we’re really shifting our offsite strategy to be much more about positive mentions in the places that AI is training and citing versus getting backlinks on high domain authority websites.
Danny Goodwin:
That is a big shift. I think still a lot of people aren’t ready for. So much of the stuff the tactics have been ingrained for – and I forget, how long have you been doing SEO roughly?
Aja Frost:
I’ve been doing SEO for a little over a decade.
Danny Goodwin:
So SEO is probably about near 30 years old at this point.
Aja Frost:
Oh, Danny, we didn’t say we were gonna talk about my age on the podcast.
Danny Goodwin:
Hey. But yeah. Um, sorry about that.
Aja Frost:
No, they’re all good.
Danny Goodwin:
So yeah, I mean, it’s just like, there’s this kind of, this whole playbook I think that a lot of people are attached to. And change is scary for a lot of people. Rethinking that stuff is important because nothing is static. And especially right now things are just kind of chaotic. The amount of changes we’re
seeing, it’s crazy.
Aja Frost:
Oh my God. Change is so scary. I think change is scary for us. We also had the pressure of not just figuring this out for our own internal strategy, but for figuring it out for our customers. The strategy that we are shipping right now, I have a very direct line to our VP of product for our marketing hub. I also spend a lot of time with the head of product for content hub. Those two products basically represent your website and content strategy and HubSpot. Everything that we’re doing. I’m telling them about the stuff that’s working, the stuff that’s not working, so they can turn that into product learnings as quickly as possible. I think it is terrifying and exhilarating and exciting all at once.
Danny Goodwin:
Yeah. And with that change, I think there’s a lot of rethinking about how we define success, right? So AEO is not going to be the same success metrics that we had with SEO. So how are you actually
thinking about that right now? It used to be like, how many links can I acquire? But what are you thinking about now? What’s important? Is it visibility in a AI answers, getting citations or mentions the actual conversions from the traffic, which again, is not as large as traffic from search, but – there is debate over whether it’s higher quality at this point, which maybe we’ll get into a little bit later. How are you sort of defining success with AEO?
Aja Frost:
This was also a topic of much debate, and we actually published the results on our Loop Marketing page.
We have a new scorecard for how companies should be thinking about marketing in the age of AI. And AEO, which fits into this loop marketing framework has a few new North Star metrics.
The first, and the one that I would argue is the most important, is visibility. And it’s visibility and not traffic, or not citations, because visibility is what’s going to ultimately inform whether someone converts. And they might not convert in that session. They’re probably not gonna convert directly from their interaction with the LLM. We know that LLMs just are really bad at navigational search. And so they’re probably opening up a new tab or maybe two days later, five days later, going to the website. But the, the visibility is what informs what we care about, which is the conversion. So that’s number one.
That takes, by the way, a lot of education with your exec leadership. And I am very lucky to work at a company, whose leadership is deeply embedded in all these conversations, and I think gets it. But if you are at a company where your CEO is not reading Search Engine Land, it’s definitely worth doing a deep dive to help them understand why visibility is the number one.
Second is share of voice. So what is your visibility like relative to your competitors? And I think that’s a really useful benchmark. I know that there was a lot of coverage back in mid-September when ChatGPT really turned down the dial on visibility for brands. And if you are just looking at visibility, you might think, oh, something’s going haywire with my strategy. If you look at share voice and share voice is constant or growing, you know that you’re doing the right thing, agnostic of some of the algorithmic changes.
Then we get to mentions, or sorry, mentions goes into visibility, then we get to citations. How many times is your website used as a source in answer engine responses? And I think this is really important. I think a lot of brands go after citations first. I’m putting it third on our list. I think it is important because if you get the citation, what we have found is your average ranking and the response and the sentiment of that description, they’re both better, which makes a ton of sense. If you control the source,
you’re always gonna say the nicest things about yourself and put yourself first. If you overindex on citations, however, you’re gonna miss out on a wide swath of visibility that I think is pretty critical.
Danny Goodwin:
You’ve done a lot of experimenting, which I want to get into in a minute, with optimizing for LLMs and AI-generated answers. What ways do you see SEO and AEO being similar? And then maybe where do you see them separating a little bit?
Aja Frost:
Yeah, I think this goes back to what I was talking about – solving for the customer or doing what is good for the end user. I think that is shared for SEO and AEO. And one of the questions you probably get, ’cause I get it all the time, is, well, if I do this for AEO, will it be bad for SEO? And my answer is always no. If you are doing, if you were rolling out an AEO strategy that is good for the end user.
So an example of what would be bad for the end user would be burying secret instructions in content for an AI agent. A good thing would be creating really helpful specific content that’s going to answer a really niche query that someone is asking ChatGPT. And as long as you are solving for that end user, I think
that you’ll benefit in both disciplines. You’ll, benefit in answer engines as well as Google.
And then I think the three higher level categories of plays are similar, but where I think things get very different are, again, the content is just, we’re going from these very broad, high level topics, these ultimate guides, which HubSpot – this is a, I don’t know, a dubious claim to fame. But when I started an SEO at HubSpot, then I was telling the blog team what keywords I thought we should target and, and recommending search friendly titles. And I really liked Ultimate Guide. I just thought it sounded nice. So every title I recommended was Ultimate Guide, this Ultimate Guide that. And then of course, a lot of websites started using Ultimate Guide, and now I’ll click through the SERPs and I see Ultimate Guide. I’m like, I think this is my fault.
So you’re going from the ultimate guide to, you know, this is the exact use case that this exact persona wants to accomplish, and here’s how to do it, and here’s some original data that we’ve gotten from customers just like you. And if you come from an answer engine, it’s gonna be tailored exactly to what we know about you. And so it’s a very different style of content and content journey.
Yeah. Yeah, yeah, for sure. ’cause I, I feel like, and I’ve, I had this conversation not publicly, but there were conversations after the whole bruhaha about all the traffic. HubSpot lost when that, that came out on, I don’t even remember what month that was this year, earlier probably in the spring. And just how much traffic they were losing. Everybody was losing their minds over it. And I was like, wow. You know, you kind of forget the influence that HubSpot had on content marketing as a whole. Your playbook that you guys came up with was used by so many other websites. Like there’s just, you know, repurposed for their specific topic or niche or whatever. But yeah, like HubSpot, that playbook was huge for a lot of years. Right. I think that’s, that was started like right before COVID around that time and then just sort of exploded., Is that the right timeframe?
Aja Frost:
I think it depends on what you are talking about. If you’re talking about inbound, inbound I think is really at the heart of the web. At least for a lot of companies that were publishing educational content and inbound goes way, way back. I think we have always been very much a build and public company and, and we share our successes and our strategies along the way. Which is what we’re doing right now with Loop Marketing. I think that has led to a lot of companies saying, oh, this was really successful for HubSpot, I’m gonna adopt it as well, which is good. That’s what we wanted.
But I also think that when we started seeing declines from the emergence of AI Overviews and the changing nature of Google, that was a bit of a bellwether for what I think a lot of websites are now seeing. And so one response could have been, oh, we’re not gonna build in public anymore. We’re gonna be very cagey about what we’re doing and what’s working. So that doesn’t happen again. But that’s obviously not what we’re doing. We’re trying to be even more transparent and helpful. I really hope and believe that loop marketing, which is not a replacement of inbound, but meant to be, again, an extension of and, and a really helpful framework for companies can play that role.
Danny Goodwin:
So just going back to that, that traffic drop. I was basically told it was about an 80% traffic drop and you kind of helped the company through that. And now in LLM world, HubSpot is the most cited CRM, is that correct?
Aja Frost:
Or the most visible CRM
Danny Goodwin:
Most visible. Okay. Gotcha. All right. And, and obviously this is, again, this is a fairly new technology. So, when you were starting to approach optimization on LLMs and AEO, how did you start that journey? Like, what were the first few things that you maybe either thought about or tried that did or did not work?
Aja Frost:
Yeah. Well, the first thing I did that I would really recommend folks do if they don’t have an AEO function already stood up was I, um, pulled together some of the ICS on our team that were already doing a lot of experimentation and research in their own time. In my day-to-day, I am usually working
with managers or directors. I’m not super close to the work. But I knew that I needed to be really close to this and really help guide it. And so I said, the three of us, we’re gonna meet once a day. We are going to launch one experiment per week if we can. I’m working with the dev team so that whatever we need to do, we can execute as quickly as possible. And so we took a very experimental mindset from the get go.
What we started out with was how do we scale good quality data-rich content? We had been thinking, and I think most people thought about content, maybe in a month you put out 30 pieces. If you’re a news publication, you could be putting out hundreds. But we’re thinking in multipliers of tens most teams. And I think we need to be thinking in multipliers of hundreds or thousands. And so with the team, I wanted to figure out how do we create that content? How do we start relatively small? So like batches of 10, generated with AI reviewed by a human, and then how do we scale that over time? That I think has been very successful.
We’re still experimenting with the types of content that get the most visibility in answer engines. And so that’s what a lot of experimentation revolves around. We also did a lot of what I think of as good clean AEO. Making sure that we were using all the available schema types across our website, making sure that things were really well structured and that we’re leading with the answer. And each section of the page is semantically complete and things are formatted in a Q and A format. You know, a lot of things that I think are now becoming like the standard AEO playbook.
Danny Goodwin:
So you mentioned content types. I know there’s been a lot of noise about how some people are abusing top X lists – the top 10 best insert thing here. Is that the sort of stuff you’ve been playing around with? When you say content form, is there anything you can share about what you found that works maybe better?
Aja Frost:
Yeah, so I’m not thinking so much about top X for Y, although I think that that still very much has a
place in people’s content playbooks. But what we’re really experimenting with is – Danny,
what’s the last thing you did research with ChatGPT to buy?
Danny Goodwin:
Oh, to buy?
Aja Frost:
Yeah.
Danny Goodwin:
Uh, it’s, it’s probably researching to find a hotel for Christmas.
Aja Frost:
Okay. Find a hotel for Christmas. So the context that ChapGPT is going to have when it recommends a hotel for you is probably about how much money you typically spend based on some demographic data it’s collected about you, if you’ve done any hotel research in the past, where you’re going, obviously how long you’re gonna stay. Hotels, we wanna provide the answers for all of those contextual clues. So if I were a hotel and I was trying to show up in answer engines, I would be creating content that spoke to your particular persona type and your particular use case. Now, I think the challenge is doing that without that content being duplicative or spammy. And to do that, this is what we spend a lot of time on. What are all the data sources that we can ingest to feed these systems essentially, so that all the content is unique, it’s grounded in what we know the persona needs, and it’s not repetitive from page to page.
Danny Goodwin:
As, as you’ve gone through this process, were there any maybe big surprises like, oh my God, I didn’t think that would work. Or is there just like any kind of aha! moments, um, as you’ve been doing all this optimization for AI answers?
Aja Frost:
The hardest part has been the measurement. I think that we are still very much as an industry, and I know this ’cause I talked to a lot of AEO vendors, figuring out how to correlate the actions that we are taking with specific visibility increases. And it’s highly dependent on the prompts you are tracking. I think that leaves the room for uncertainty and ambiguity because what if you’re tracking the wrong prompts? Or what if you’re tracking the right prompts, but not enough of them? It’s far less clear to say “I did X and Y happened” than it was with SEO. And even with SEO, you know, we couldn’t run A/B tests. We are always doing look backs. There’s so many variables at play.
I talked about education with execs around why visibility is the most important. I think the other really important piece of education, not just for executive leadership, but for, SEO/AEO teams is getting comfortable with less data and fewer direct lines between what we’re doing and the results. So that’s been, I don’t know if that’s been surprising ’cause I think I knew going in that that was going to be hard. But as we’ve progressed and we’ve done more and more teasing apart, the impact of individual experiments has gotten harder and harder.
Danny Goodwin:
So I heard through on background of getting this interview set up that you sort of have a formula for getting ChatGPT to recommend a brand. So I want to hear all about that. What can you tell us about that?
Aja Frost:
Well, I think that many of the best tactics that we are successfully using are ones that I’ve already mentioned. So we’ve spent a lot of time talking about hyper-specific persona-centric content. What we’ve talked about a little less is the off-site tactics that we’re using. And what we’ve done is identified ChatGPT and Google, because those are priority engines, we’ve identified their top training and citation sources. And then we have put together a concerted strategy to show up as positively and frequently as possible in those places. And two big areas for us have been YouTube and Reddit, which probably won’t surprise anyone as being very influential for answer engines. I can go a little bit more into some of the things we’ve done there, if that’s useful?
Danny Goodwin:
Yeah, I think so. There’s been some research done around how heavily cited Reddit and YouTube and a few other sites are. So yeah, I’d be kinda curious to know, like from a strategic standpoint, maybe like how you guys are approaching Reddit and YouTube.
Aja Frost:
Yeah. Very different strategies for each and one big learning for us, I wouldn’t say this is in the last year because we’ve been very active on both platforms for several years, but, um, treating every social
media platform as its own beast and really getting to know the lay of the land and understanding the culture and the rules and the unspoken rules before we engage. I mean, that’s just a general best practice for any community or social media site.
But on YouTube, uh, we have a large slate of owned channels from Marketing Against the Grain and HubSpot Marketing, to how to HubSpot, science of scaling. It really runs the gamut. And we, the global growth or SEO AEO team works really closely with the teams creating those conthat content to weave in organic mentions of the products where they make sense and make sure that we are creating content on topics that we know answer engines and people care about. We also have a lot of creator partnerships with folks who speak to our relevant audience and somewhat similar playbook there. We want organic, relevant, contextual mentions of HubSpot.
Danny Goodwin:
So that’s like influencer marketing, that sort of thing when you say creator?
Aja Frost:
Yeah. I think you could call it influencer marketing. I mean, we, we sign, um, multi-month sometimes one-year contracts with creators and, and say, you know, we will pay you X, Y, Z and, in exchange you will create content on these wide topics. Well, we give them a lot of editorial freedom, but you know. You’ll mention HubSpot in X videos, that sort of thing.
And then on Reddit, it is a much more advocacy and community-centric approach. And I should have shouted out HubSpot Media on the YouTube front. They are a fantastic partner to my team. On the Reddit front, we work really closely with HubSpot community, another internal team. And in the last year we became the co-moderator of HubSpot’s subreddit. And we have spent most of our time making that subreddit as productive and engaging as possible because what we’ve seen, which is really interesting, is that the more activity that happens in our HubSpot, the more positive mentions of HubSpot there are across Reddit. Because basically you’re creating a team of advocates who are really excited about your brand, your product, and then they organically go out into conversations on our sales, our marketing, our CRM, and they say good things about HubSpot. So, very, very different strategies, but both focused on getting the right people to say nice things about HubSpot.
Danny Goodwin:
I think we touched on this a little bit earlier. Google search versus traffic you get from AI engines, it’s very different. It’s not as large. We’ve actually reported, in the last couple months, three different stories basically saying that traffic that you get from LLMs is either worse or about on par with Google search in terms of converting. I’m curious what you’ve seen there. Do you see that to be the case or do you see quality traffic coming through?
Aja Frost:
Yeah, the traffic that directly comes from LLMs converts at about three times better than traditional search for us. So we’re definitely seeing higher conversion rates. And I, I’ve read the SEL stories. I was looking at the one you most recently published, which was like 900 e-comm website over the course of a year. I shared that with my team last week. I was curious whether the difference in conversion rates had anything to do with the difference in the type of product and the buying journey. Like, I think by the time someone is coming to hubspot.com from an LLM, they’ve done a lot of research, at least that’s what our analysis suggests. And so they’re much readier to convert than someone who might in the old world have been coming to the blog to download an ebook on content marketing. It’s been another really fascinating area to watch the industry debate because I’ve also seen several different, uh, different stats.
Danny Goodwin:
Right. Yeah. Again, it’s very early and these are not large scale studies, it’s just sort of anecdotal I guess we would say. But any data, I think is useful ’cause at least it gets people thinking about all of these things and it’s gonna always go back to, it depends. It may be different for ecomm versus B2B or whatever the case may be. I think there’s still a lot that’s going to change and where AI is now. I even today was seeing somebody saying we’re at peak AI already. Like really? Like it’s, it’s two years old. Like, come on.
Aja Frost:
Yeah. I would disagree with that. Yeah. I think there are, to your point, some things that could be step function increases in conversion rates. Obviously instant checkout, that’s huge. I think that, yeah, I mean this was obviously over the course of a year and I do remember seeing in the study that conversion rates had increased over time, maybe as people got more comfortable or familiar with ChatGPT. But instant checkout’s huge. I don’t know what adoption for Atlas is going to be or for any of these ad browsers to be fair. But agent mode or agentic checkout would definitely improve conversion rates. So I think we’re at the very early innings of this.
Danny Goodwin:
Where do you think AEO as a practice will be at maybe a year from now? Do you think it’ll be kind of its own thing? Do you think it’ll be part of SEO and is there anything that you were maybe kinda excited to see happen from ChatGPT or some of these other engines that could make these systems even better?
Aja Frost:
I think a lot hinges on when Google makes AI Mode more of the primary search experience. I don’t believe that you are going to get an AI-powered answer for every search. My belief is for navigational queries, at the very least, you’re probably always gonna have something that feels like the traditional SERP and that it gets you from point A to point B very quickly. But I think for a lot, if not most other searches, you will probably be in some form of AI Mode and at that point, SEO and AEO become merged because there is no real traditional SERP to optimize for anymore.
Danny Goodwin:
Yep. Exactly. That’s sort of been my problem with this whole naming debate. If you’re gonna call it AI SEO, what happens if that search engine goes away? There’s no more, there’s no more SE in SEO.
Aja Frost:
Totally. Yeah. But yeah, and also that doesn’t exactly roll off the tongue. Like I don’t wanna stand up and and say I am an AI SEO.
Danny Goodwin:
Right. Exactly. So if you could maybe give people one AEO type of experiment you think maybe they could run before the end of the year to kinda get a feel for it or just anything that you think might be helpful for them to kinda experiment with. Is there anything maybe you could suggest to people like, try this tactic or this strategy or whatever?
Aja Frost:
I think if you want a real project, then I would try creating those hyper-specific, very persona-focused pages. I think if you’re looking for something that you could run with and get live by the end of the week, use one of the many query fan-out tools that are available online. Take a page that already exists on your website, plug like a, a likely reasonable query that would lead someone to that page into a query fan-out pool, and then assess whether your page answers or has content for all of the subqueries that that pool provides. And if it doesn’t add them and then see does your visibility for that head question increase.
Danny Goodwin:
Awesome. Any final thoughts? Anything we didn’t talk about that you’d love to comment on or leave people with some parting words of wisdom?
Aja Frost:
Yeah, I would, I would be remiss not to direct people to hubspot.com/loopmarketing. We have spent a lot of time on AEO. Of course, AEO is one of the tactics in this new growth framework for the AI era, but there’s a lot more that we believe businesses can and should be doing to not just survive but thrive. Check it out. I think there’s a lot there.
Danny Goodwin:
Awesome. And just, just for anyone who’s listening and doesn’t know what is loop marketing like, can you give us just a quick overview of what that is? ’cause you mentioned a couple times.
Aja Frost:
Yeah. Loop marketing is a growth framework for businesses. There are four phases: express, tailor, amplify, and evolve. Each of those four phases has a host of plays and tactics. But the general idea is that, as the web changes, as folks go from progressing through this ever narrowing funnel to
getting an answer in an LLM, then going to your Instagram, then reading a review and, and really having like a much more messy, much less linear journey, we need a new framework for marketing. And so this framework is an ever-evolving, much more flexible dynamic framework.
Danny Goodwin:
Right. So it’s sort of like that old bendy straw, the messy middle as Google put it, I think. Right?
Aja Frost:
Yes. Yes. I will say messy middle came up many times in our conversations around the loop.
Danny Goodwin:
Yeah. Awesome. Alright, well that is all the time I have for you for today. It was a great conversation. I really appreciate you taking the time to chat with us. Look forward to seeing more from you in the future and wishing you nothing but success heading forward.
Aja Frost:
Thanks so much, Danny. This was really fun.
Danny Goodwin:
All right. Thanks. Aja. Bye everybody.
Read more at Read More









 director at Deviation, summarized it nicely to me, sharing:
director at Deviation, summarized it nicely to me, sharing: